TMJ and Ear Pain - Causes, Symptoms, Treatment
One of the leading symptoms of temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders is ear pain. In fact, it is one of the more commonly reported symptoms. Your temporomandibular joint is connected to many of the muscles found in the maxillofacial region and as a result, a problem with your TMJ can cause pain across your face. Fortunately, experts like Dr. Katherine Phillips can provide TMJ disorder treatment, thus providing lasting relief.
What is TMJ?
The TMJ are the joints that connect your jaw to your skull on each side of your head just below your ears. Acting as a sliding hinge, moving side to side, up and down, and back and forth, they enable you to chew, talk, yawn, and more. Due to overuse, when injured, or when certain medical conditions affect your TMJ, TMD-related inflammation, pain, and swelling can wreak havoc on your quality of life. The pain and discomfort of TMD is not surprising when you consider how often you use these complex joints.
What are the symptoms of ear pain from TMJ?
The maxillofacial region, which includes the TMJs, is immensely complex and closely interconnected. Just think about the many different facial expressions you can make and the many ways you can move your jaw and mouth. The intricate system of muscles, joints, and other tissues of the maxillofacial region make all this possible. You can click here to learn about the basics of your TMJ and how it functions.
This intricacy also means TMJ disorders (TMD) can cause pain and other complications across the face. Since your ears are located less than a half an inch from your TMJs, this includes ear pain.
Symptoms of ear pain from TMJ Ear pain might be a dull, ongoing irritation or it could be a sharp, searing pain. The pain may worsen with jaw movement, although not always. Inflammation and swelling due to TMD can spread to the ear causing ear pain. Additionally, straining the muscles connected to the TMJ can result in ear pain as well as tension headaches and pain behind the eyes.
By addressing the TMJ disorder, you may be able to address pain in your ears and elsewhere. If your ear pain is the result of a TMJ disorder, treatments that target only the ear, or ear infections, may be ineffective.
What are the causes of ear pain due to TMJ?
Inflammation in the TMJ
As with any joint in your body, when the TMJ is overused, injured, or are afflicted with a chronic condition such as osteoarthritis, it and the muscles around it can become inflamed. Generally speaking, inflammation is the body’s immune system’s response to an irritant. Although the inflammation originates in the TMJ, it can spread to tissues and muscles surrounding the area, including the ear.
Swelling in the TMJ
Swelling and inflammation usually go hand-in-hand, and blood flow to an affected area increases with inflammation. This can result in a buildup of fluid not only inside the TMJ, but in surrounding tissues. This buildup causes swelling, signified by an increase in the size or a change in the shape of the affected area.
Overuse putting pressure on the TMJ
The TMJ is one of the hardest-working joints in your body. You use it to talk, eat and drink, yawn, and even when you open your mouth to breathe or sigh. Overuse and subtle muscle spasms caused by teeth grinding (bruxism) and clenching, and repetitive actions such as chewing gum, puts extra pressure on the TMJ. This may result in inflammation and swelling. Pain and tenderness in the TMJ due to overuse can radiate to surrounding tissues, including the ears.
Stress
Being under stress can cause you to clench and/or grind your teeth which puts extra strain and pressure on your TMJs. These actions can cause stress-induced TMJ disorder.
Presence of osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis in the TMJ
Osteoarthritis is the most common form of degenerative arthritis. It can affect every joint in the body, including the TMJ. Osteoarthritis of the TMJ affects both the hard and soft tissues around the TMJ, changing the shape and functioning of the jaw.
Rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic, autoimmune disease. It attacks the lining of the TMJ causing it to become inflamed and damaging the joint tissue.
Do I have an ear infection or TMJ related ear pain?
To properly diagnose whether your ear pain is the result of an infection or TMJ disorder-related, you should consult a medical professional. However, be aware there are some important differences between the two types of pain.
TMJ-related ear pain is most often felt in front of or below the ear. With ear infections, the pain is often inside the ear. If the pain sharpens when you move your mouth, this may also indicate a TMJ disorder is resulting in ear pain. Also, check for the TMJ disorder symptoms below, or see our TMJ disorder symptoms page.
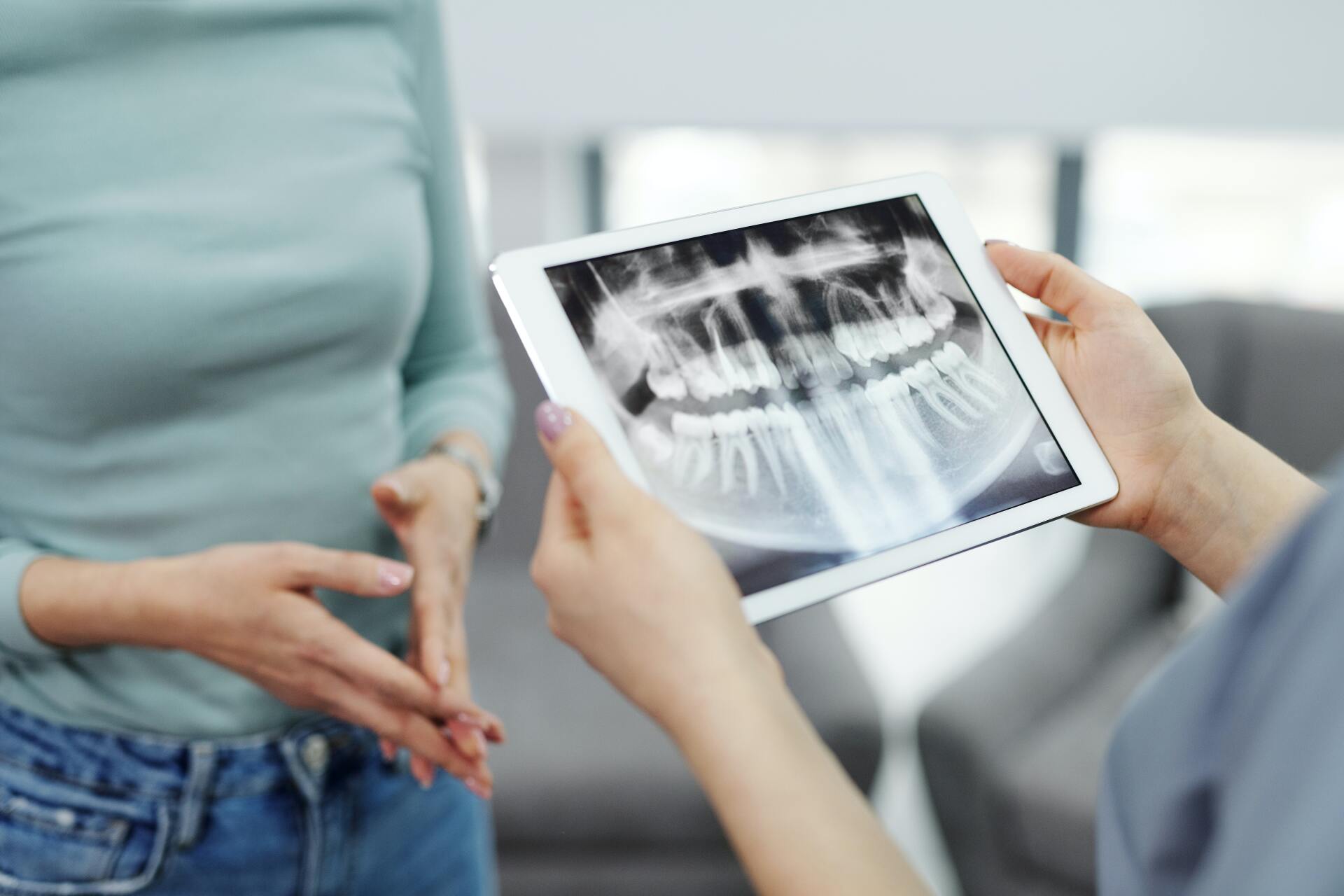
Often, it’s best to first rule out ear infections. A quick visual inspection is usually enough to diagnose these infections. With TMJ disorders, the most effective way to diagnose a problem is with a Cone Beam CT Scan, which produces a 3-D image of your jaw joint, combined with a physical examination of a doctor experienced in orofacial pain and TMD.
What are some of the other symptoms of TMD?
While many people rightly associate jaw pain with TMJ disorders (TMD), the nature of the temporomandibular joint means pain can turn up elsewhere, including the ears. In fact, ear pain is one of the most common symptoms of TMD. Likewise, the most common cause of ear pain in adults is TMD, not ear infection.
Other symptoms of TMD include:
- Jaw pain
- Headaches
- Clicking or Popping sounds when moving the jaw
- Locked jaw or limited range of motion
- Ear fullness
- Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
- Pain behind the eyes
- Neck and shoulder pain
- Other orofacial pain
What treatments exist for ear pain associated with TMJ?
Fortunately, it is possible to both diagnose and treat TMJ disorders. It’s important to seek professional help if you are suffering from a TMD as the disorders are easy to misdiagnose and mistreat. Further, each TMD will require its own treatment plan. While cases may be similar, they are never identical. Let’s look at some of the more effective types of treatments .
Home Exercises and Stretches for TMJ
There are a variety of home exercises and stretches that you can perform to strengthen your jaw and the connecting muscles. Over time, this could provide pain relief. One of the simple things you can do to relieve TMJ pain is practice holding your lips together while keeping your teeth separated. In this position, the TMJ isn’t engaged. Stretching exercises such as those below also help with pain relief.
- Close your mouth. With your head facing straight ahead, glance to the right with your eyes only. Extend your lower jaw to the left and hold for 5-10 seconds. Repeat on the opposite side.
- With your shoulders back, chest up, and jaw relaxed, pull your chin straight back, creating a “double chin.” Hold for three seconds and repeat 10 times.
- Touch your tongue to the roof of your mouth, then slowly open and close your mouth.
- Slowly open your mouth as wide as you comfortably can while holding your tongue in a neutral position. Hold in place for 5 to 10 seconds. Close your mouth then open it again slightly. Gently glide your jaw back and forth five to 10 times.
Additionally, you can gently massage your TMJ and the surrounding muscles. A hot or cold compress can provide immediate relief. And if you’re eating hard, crunchy foods, it’s time to change your diet. Opt for softer, easier to chew foods that won’t strain your joints and muscles.
If you want to massage your TMJ or use strength-building exercises, it’s smart to talk to a professional. He or she will be able to teach you how to perform these exercises appropriately.
When should you see a medical professional for TMJ ear pain?
Seek attention from a TMJ medical expert such as Dr. Katherine Phillips if you have persistent pain or tenderness in your jaw, which may be accompanied by ear pain and other symptoms. Untreated or undertreated TMD can lead to a host of long-term issues, including blocked eustachian tubes and possibly hearing loss. Your TMJ specialist can discuss possible causes and treatments for your problem
Why it's important to work with a TMJ specialist.
TMJ disorders can be extremely complex. The symptoms are often diverse and vary from case-to-case. So too does the underlying cause. A treatment plan that addresses the TMD in one patient won’t necessarily treat the pain in another patient.
If you are suffering from ear aches and exhibiting TMD symptoms, you should consider working with a professional. He or she may be able to:
- Provide physical therapy
- Teach you how to perform strength-building exercises
- Prescribe anti-inflammatory drugs and muscle relaxants
- Build custom bite orthotics to realign the jaw and reduce stress on the jaw joint complex.
In some cases, surgery may be required or other treatment plans will have to be devised. Lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking, may also help. A TMJ disorder specialist can work with you to develop an effective treatment plan that will resolve your disorder and provide pain relief.
How do doctors diagnose ear / TMJ related jaw pain issues?
TMJ disorders are often difficult to diagnose because the symptoms can mimic those of other medical conditions. Due to this, many sufferers go undiagnosed or underdiagnosed for years until they see a TMJ expert.
TMJ dentists take a detailed medical and dental history, and examine problem areas. Signs of overuse, such as worn down and cracked teeth due to grinding, will also be evaluated. As previously mentioned, a quick visual inspection is usually enough to rule out an ear infection. Diagnostics usually include imaging, such as advanced 3-D Cone Beam CT imaging or digital X-rays.
When seeing your TMJ dentist, keep in mind:
- Recent dental surgeries. Lengthy dental work that requires your mouth to be open wide for extended periods of time can cause or aggravate TMD.
- Illnesses. Other health problems that coexist with TMJ disorders, such as chronic fatigue syndrome, sleep disturbances, or fibromyalgia.
- Injuries. Just like other joints in your body, the TMJ can be injured which may lead to TMD.
- Changes to your mental health, such as stress, anxiety, or depression. When you are anxious, depressed, or stressed out, you may unknowingly tense up, clench your jaw, and even grind and gnash your teeth at night (bruxism). This puts extra pressure on your hard-working TMJs, resulting in over-use which can lead to pain and tenderness in the area and the joint itself.
Your dentist will examine your jaw, looking for the following:
- Listen to your jaw. Damaged cartilage tissue can cause a popping sound and clicking sounds in the TMJ.
- Feel your jaw and around your face. Swelling along your jaw and throughout your lower face is a symptom of TMD. It can occur on one or both sides.
- Look in your ears. Checking inside the ears helps rule out an ear infection.
- Examine your mouth. Cracked and worn down teeth are signs of bruxism (teeth clenching and grinding), which can cause TMD due to overuse.
Answering Your Frequently Asked Questions
Can TMJ disorders cause ear fullness and/or pressure as well?
TMJ disorders can result in a sensation of pressure or fullness in the ear, as well as other conditions such as tinnitus (ringing in the ears). The causes may include nerve irritation and changes at the base of the skull, or dysfunction in the muscles of the neck associated with TMD.
Can TMJ issues affect your hearing?
TMJ disorders may affect your hearing. It’s thought that pressure or inflammation from the TMJ can affect nerves and muscles in the area, leading to blocked eustachian tubes. When fluid cannot properly drain from the middle ear, it may result in difficulty hearing.
Is my TMJ related ear pain permanent?
Ear pain due to TMD does not need to be permanent. Successfully treating the causes of TMD and effectively managing TMD flare-ups can reduce TMJ pain and inflammation. This can reduce or eliminate any associated pain in surrounding tissues, including the ear.
Can the TMJ cause swelling behind or under the ear?
TMJ pain that radiates to ear pain is most often felt in front of or below the ear instead of inside the ear. This is because the TMJ is located below and just in front of the ear.
Does clenching my jaw cause ear pain?
Jaw clenching puts pressure on the muscles, tissues, and other structures around your jaw, including the TMJ. Excess stress on the TMJ can cause TMD, resulting in inflammation and swelling which can affect areas surrounding the TMJ, including the ear.
Are You Experiencing Ear Pain?
Dr. Katherine Phillips is a leading TMJ disorder specialist. Over the last 13 years (as of the publication of this article), she has treated thousands of patients suffering from a TMD. Using her vast experience and education, Dr. Phillips can help you devise a treatment plan that will provide both immediate and long-lasting pain relief. Get in touch today!
Contact Us Today For A Consultation!
Contact Us
Thank you for reaching out to us at REstore TMJ and Sleep Therapy. We look forward to helping you. We will follow up within 24 hours for contact requests received during normal office hours Monday – Thursday. If you have submitted a request later in the day on Thursday – Sunday, we will follow up on Monday. If you would like to talk to us before we can get to your request, please feel free to give us a call at 281-296-6797 Monday – Thursday 8am – 4:30pm. Have a great day!
Regards,
Dr. Katherine Phillips and Staff
Please try again later.
REstore TMJ & Sleep Therapy P.A.
1001 Medical Plaza Drive,
Suite 200 | The Woodlands, TX 77380
281-296-6797
Dr. Phillips serves TMJ & Sleep patients in: The Woodlands TX | Spring TX | Conroe TX Tomball TX | Cypress, TX | Houston, TX | Kingwood TX | Humble, TX | Katy TX
© 2023 by REstore TMJ & Sleep Therapy | Terms Of Service & Privacy Policy | XML Sitemap
-2700x842-1920w.png)